Ora beats UWorld by 3x in biggest MedEd RCT ever
Research paper coming soon!
UWorld
- Traditional QBank
- 8,000 available questions
- Manual study plan
- Spaced Repetition QBank ™
- 30,000+ available questions
- AI-optimized study plan
The only evidence-based study platform that guides you from M1 to MD.
Designed by top doctors & educators



"I love Ora, I tell all my classmates to use it. It's difficult to know what you don't know, but with Ora, you don't have to think about what to study - AI does it for you, so you can just sit down and start doing questions."

"This is a smarter UWorld. It has UWorld-equivalent questions, and it quickly identifies your weaknesses and builds a regimented plan to help you attack them. It's basically a blend between UWorld and Anki."

"Ora considers the learning science behind every detail..."

Research paper coming soon!
Backed by leading investors





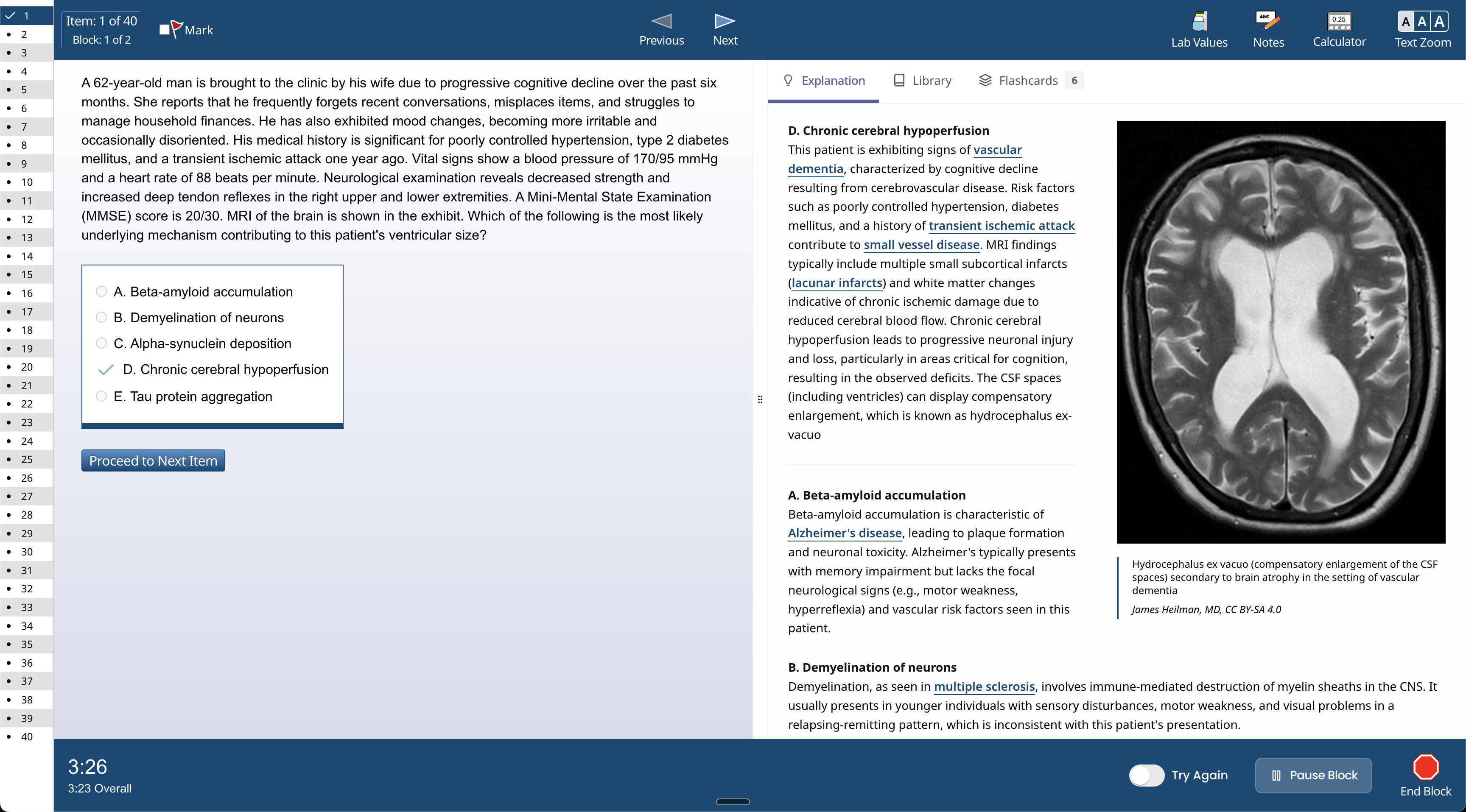
Ora can help you prepare for any exam in med school.
Ora has the tools to get you ready for any exam.
Mimics the real exam experience
Spaced-Repetition using FSRS
Fundamentals for over 300 topics
Ask Ora AI about any medical topic
In-depth explanations of concepts
Focus on your weaknesses—not your strengths.
Flashcards backed by FSRS, the most advanced spaced-repetition algorithm available.
Ora has over 300 videos to help you learn the fundamentals of medicine.
AI chat is integrated right into the QBank and flashcard experience,
making it easier than ever to get your questions answered.
Explore a meticulously curated repository offering an extensive collection of medical education content, designed to support your learning journey.
Explore the Library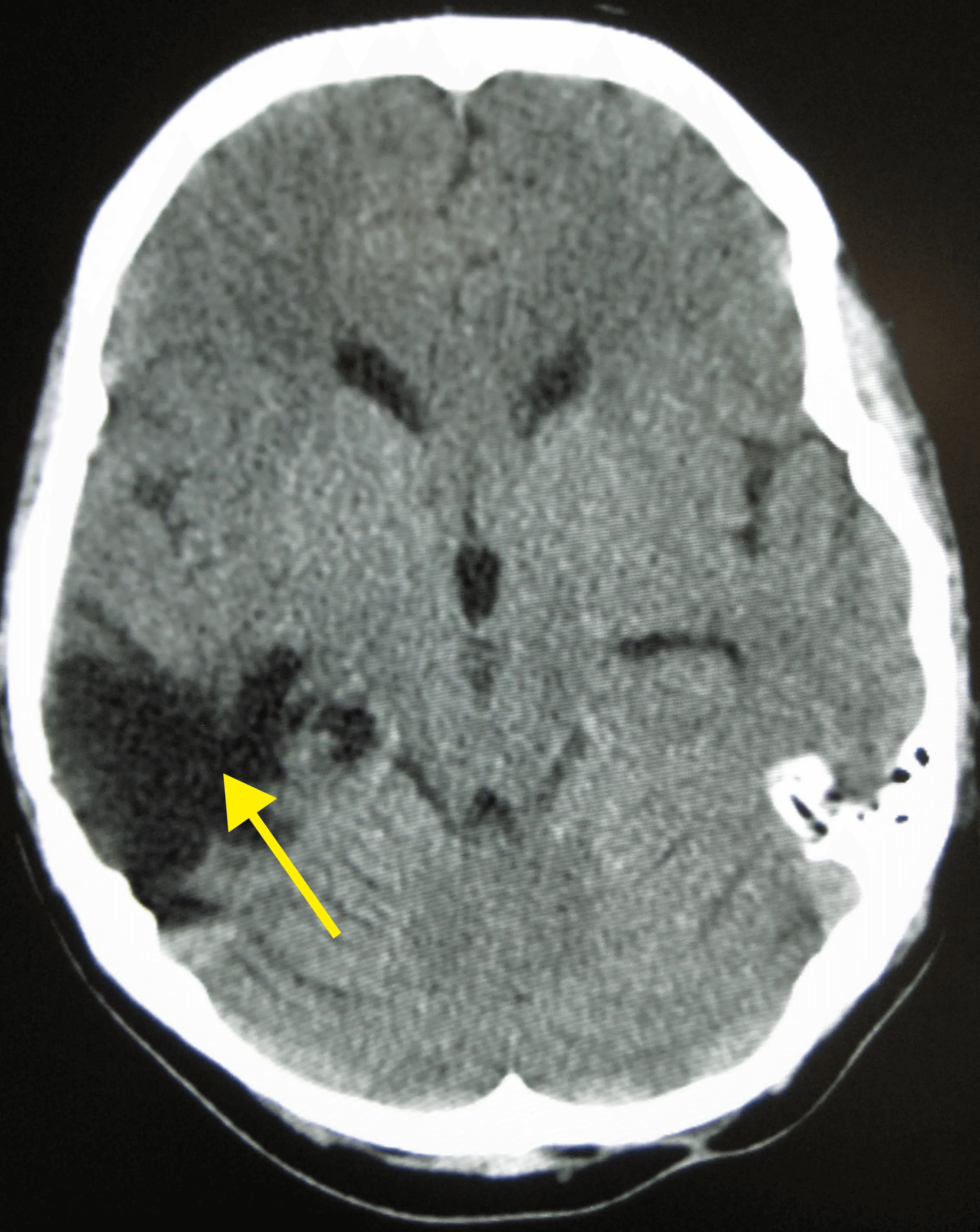
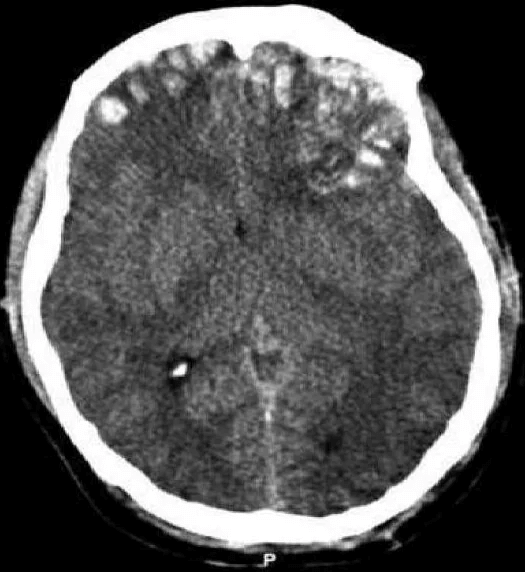
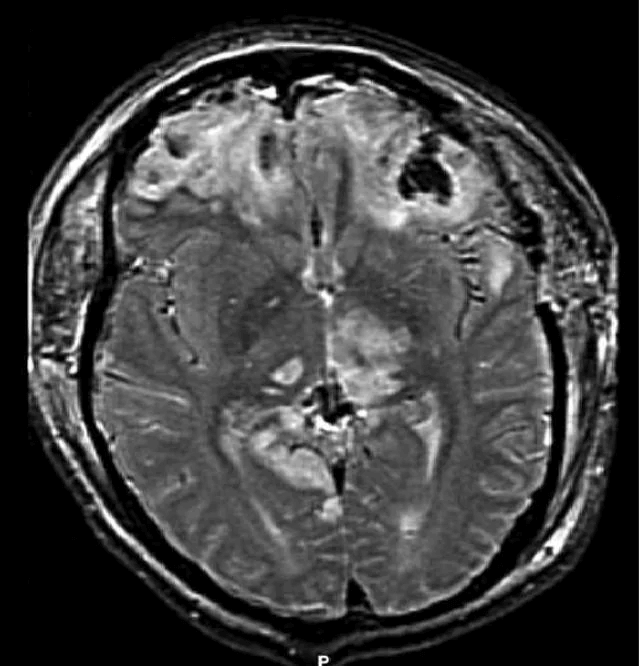
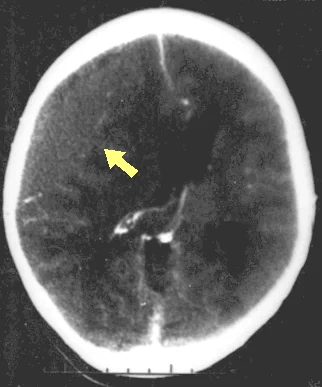
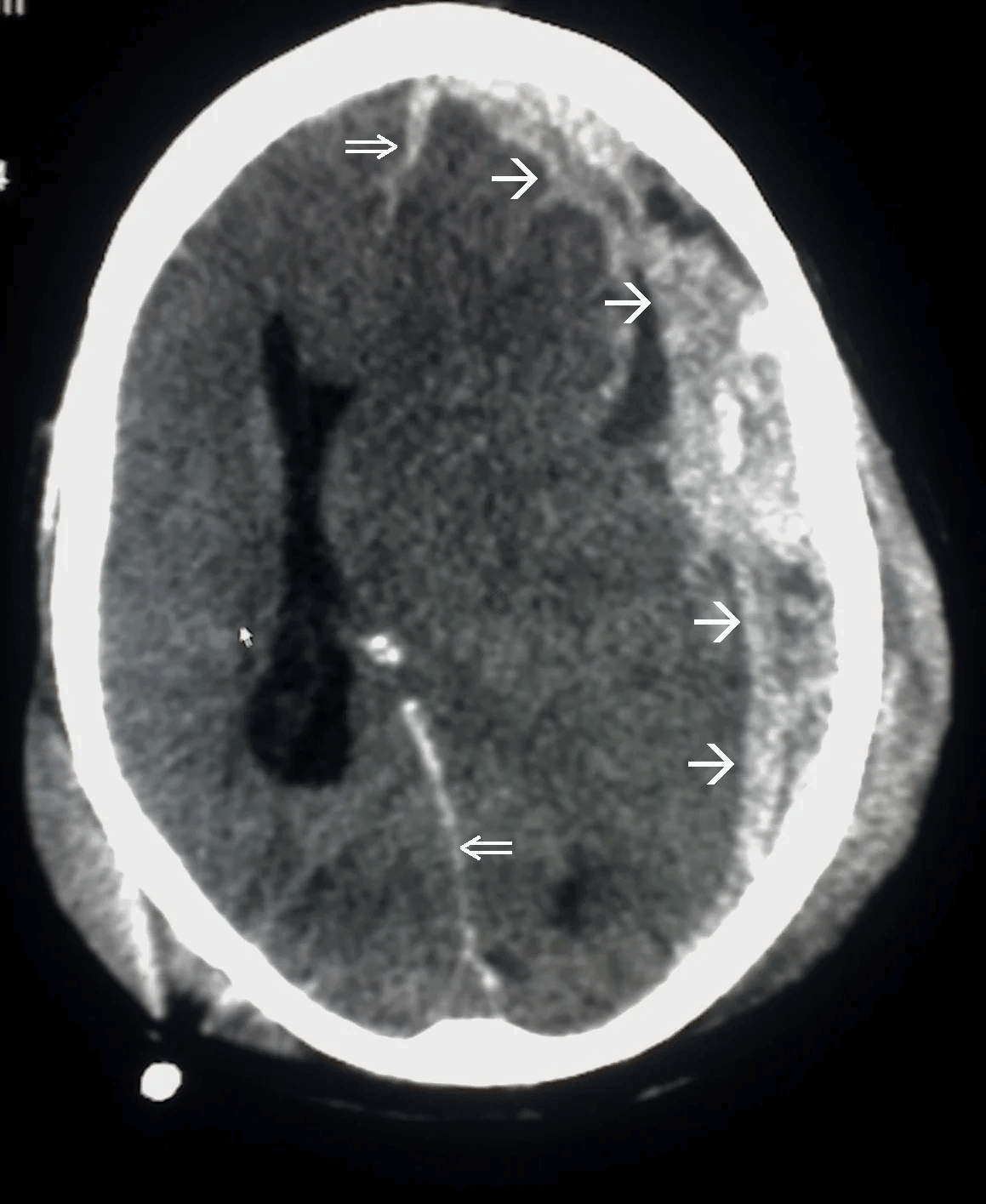
Disruption of brain function due to external mechanical force, involving:
These processes lead to neuronal damage, cerebral swelling, and compromised cerebral perfusion.
Other features may include seizures, vomiting, altered mental status, and signs of skull fractures (e.g., CSF rhinorrhea).
Additional workup may include MRI for diffuse axonal injury, laboratory tests, and intracranial pressure monitoring.
Preventing secondary injury involves maintaining adequate blood pressure, seizure prophylaxis, and temperature management.
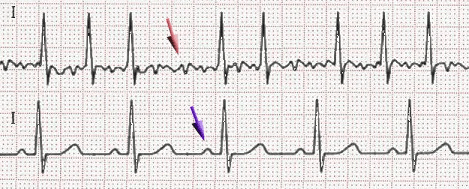
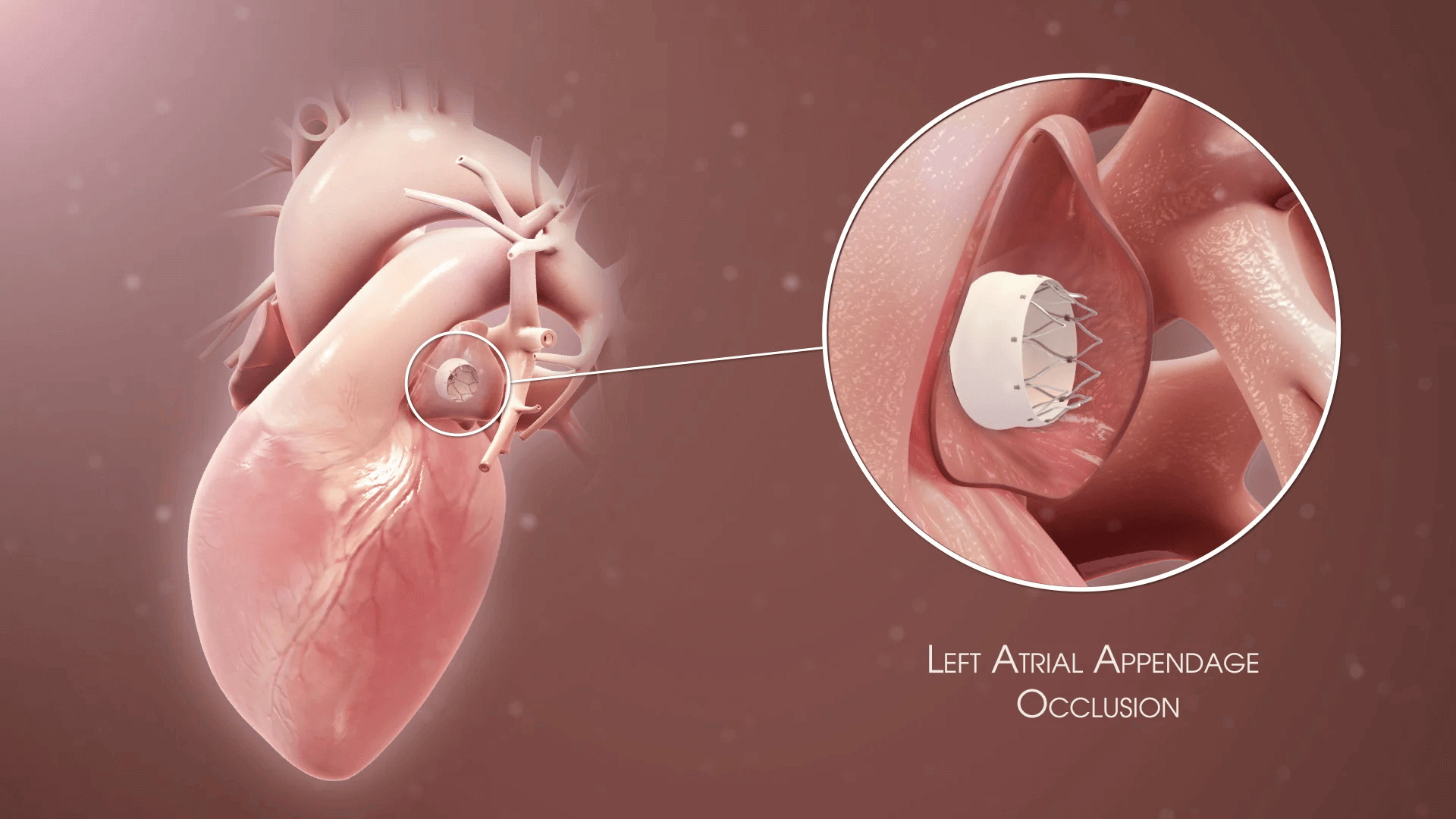
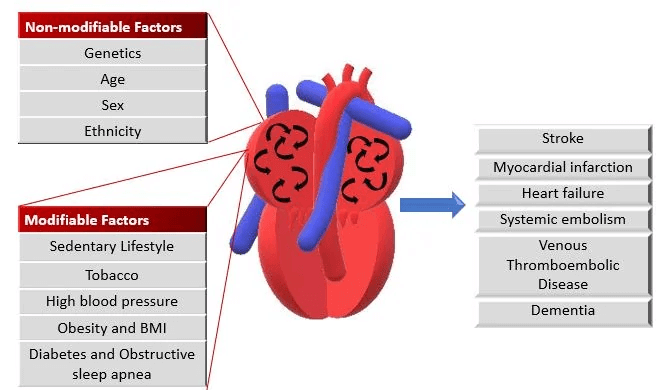
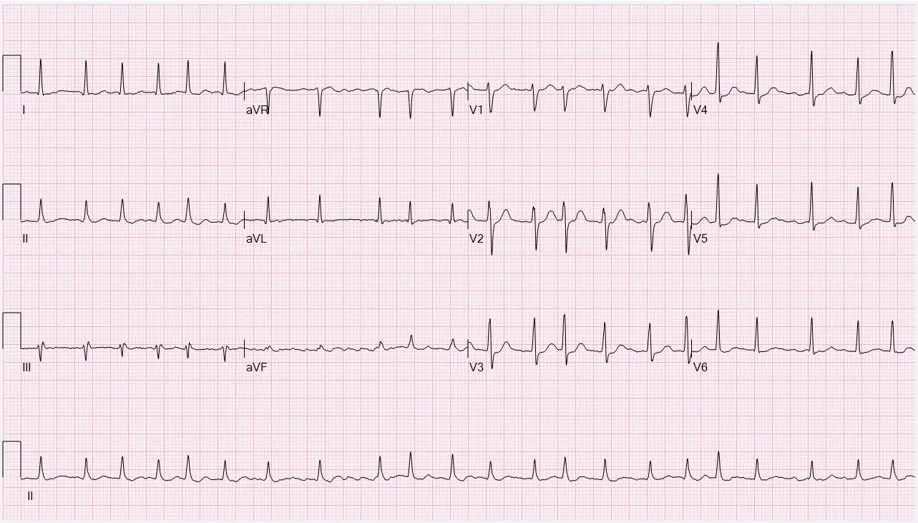
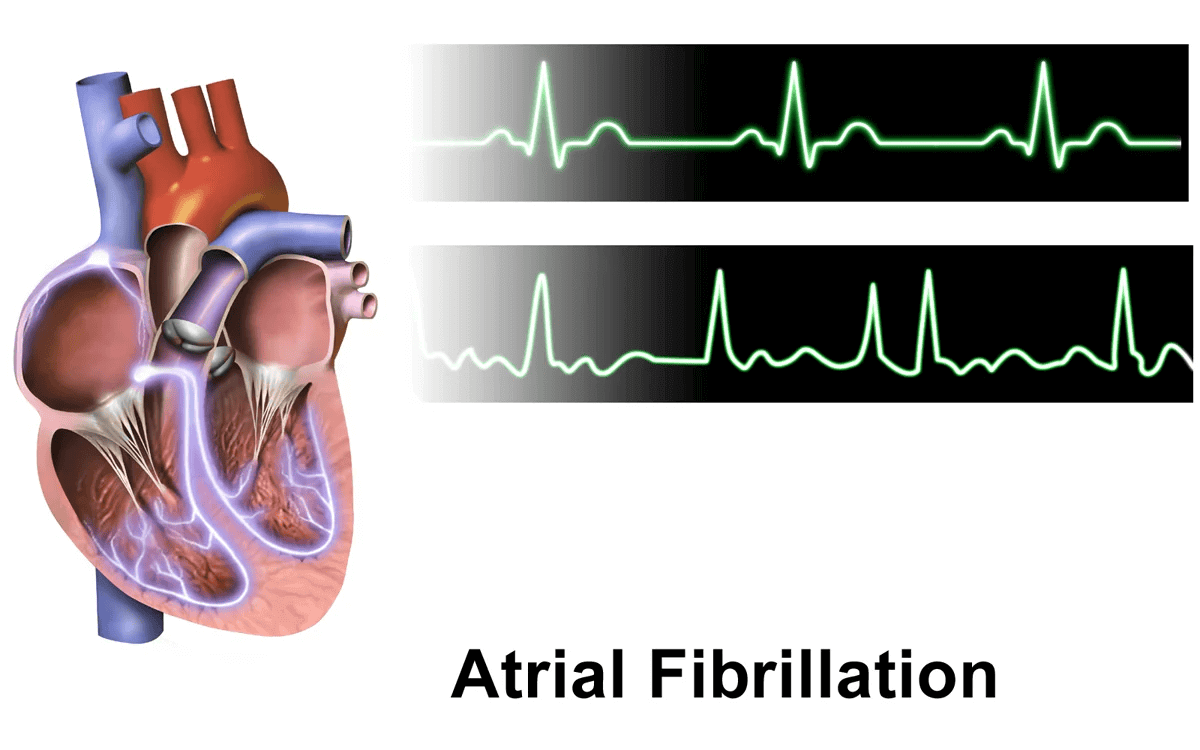
Uncoordinated atrial activation leads to ineffective atrial contraction and an irregularly irregular ventricular response. Key mechanisms include:
Electrical and structural remodeling of the atria promote AF persistence ("AF begets AF").
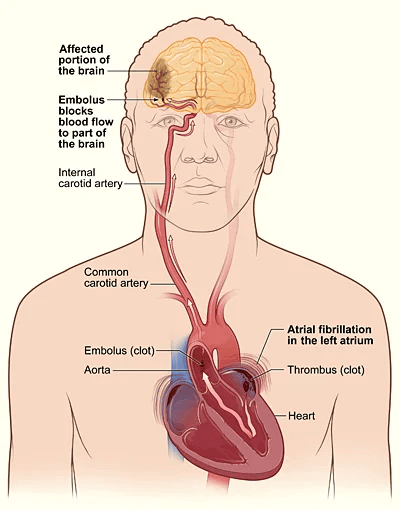
Patients may also experience dizziness, chest discomfort, or be asymptomatic. AF increases the risk of thromboembolic events, such as stroke.
Additional tests include thyroid function tests and evaluation of stroke risk using the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
Rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs, electrical cardioversion, or catheter ablation may be considered in symptomatic patients or those with heart failure.
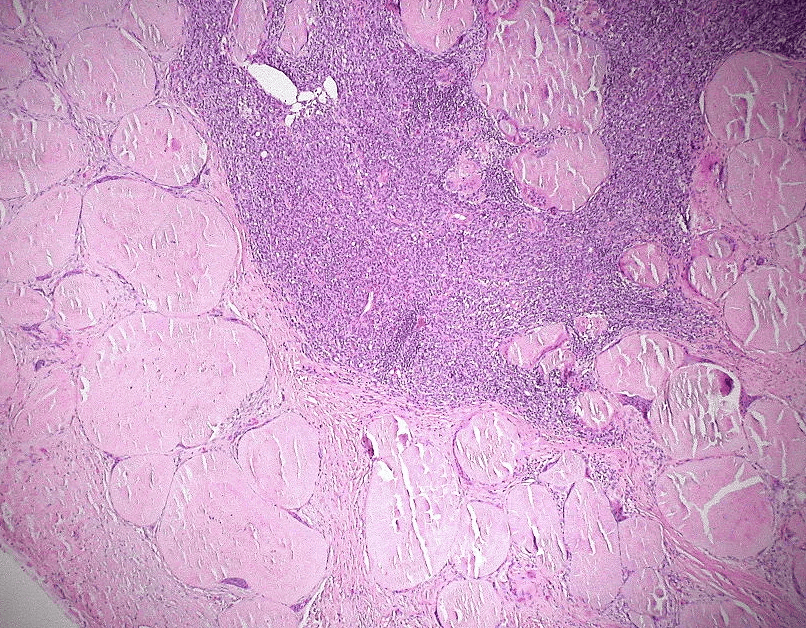
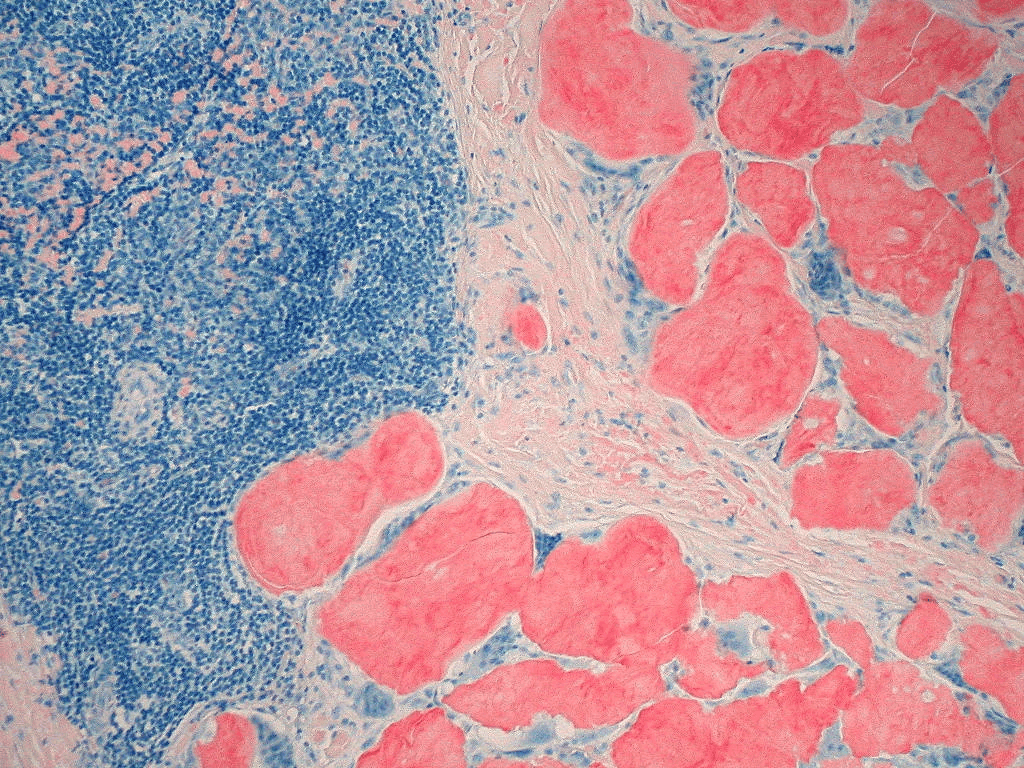
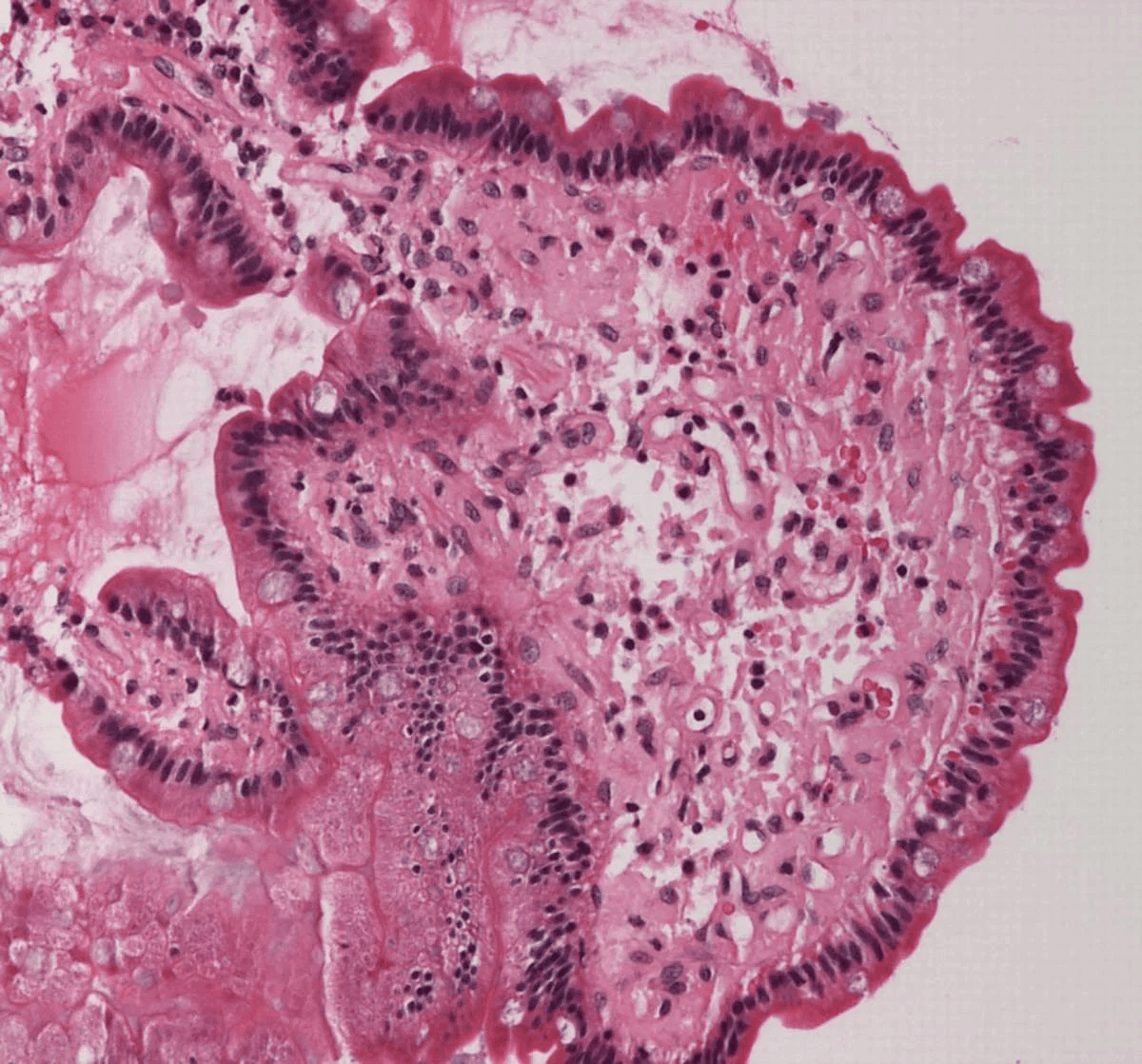
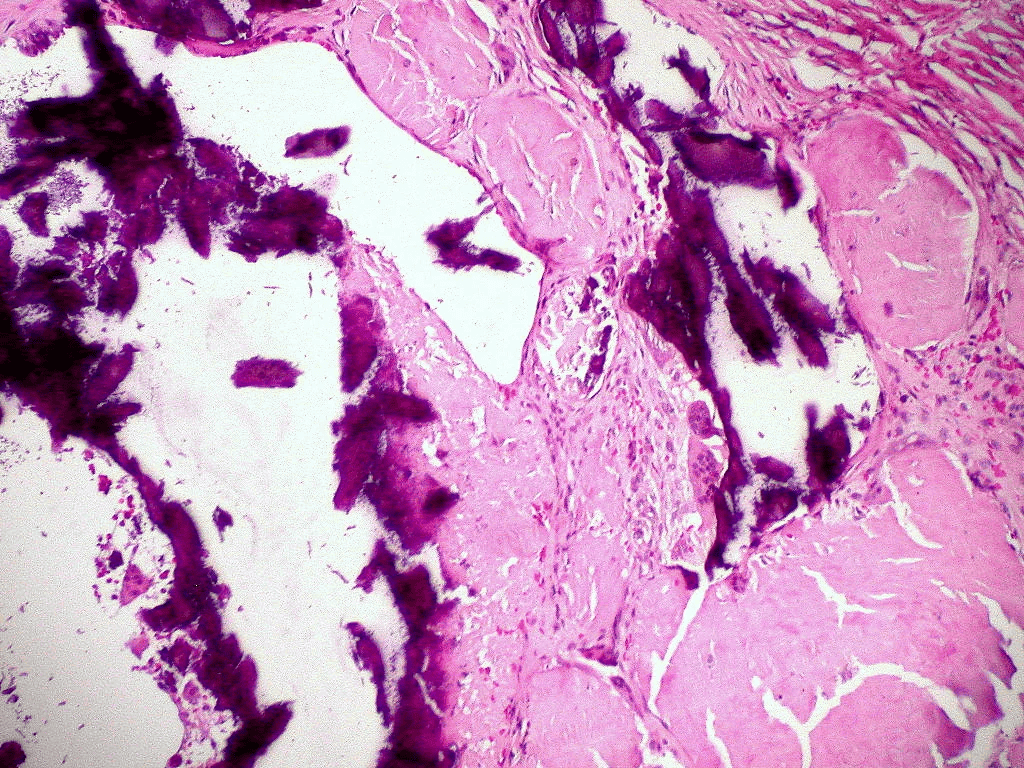
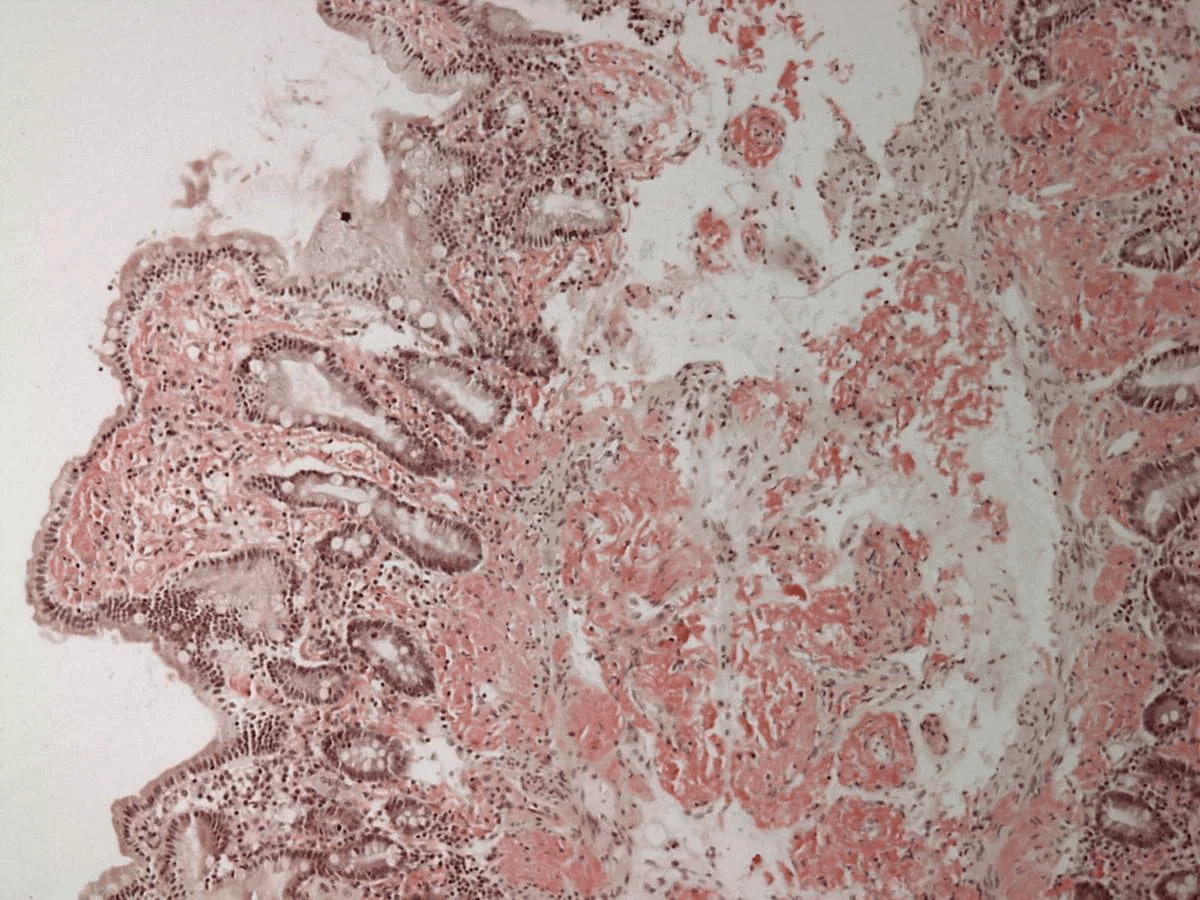
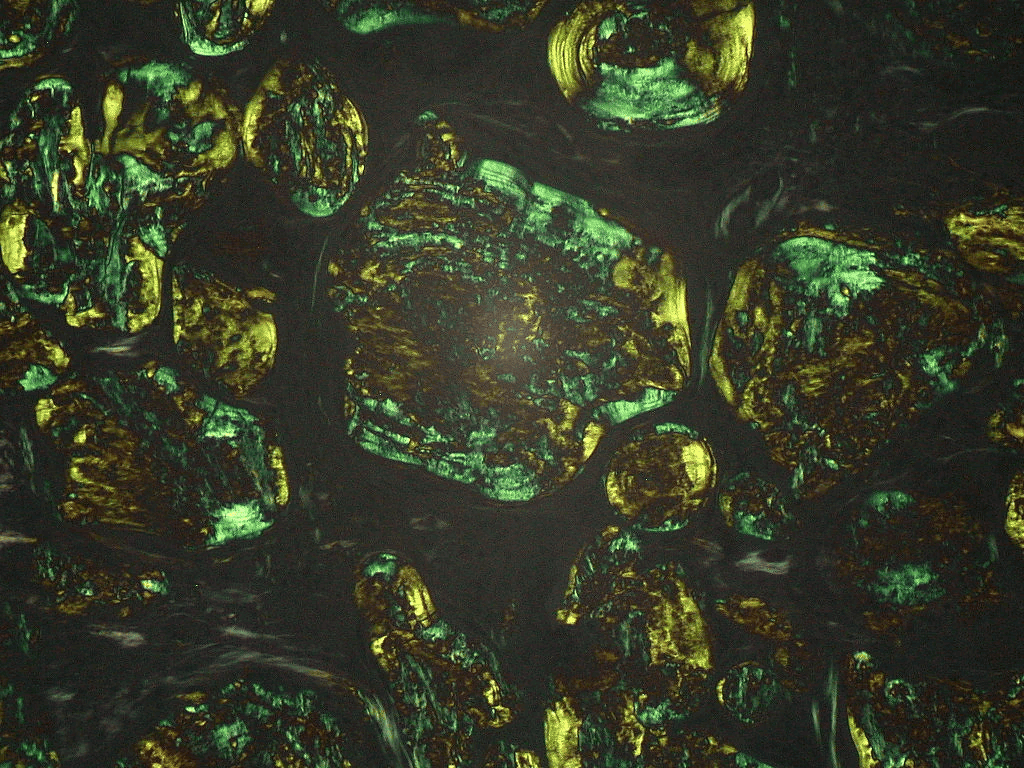
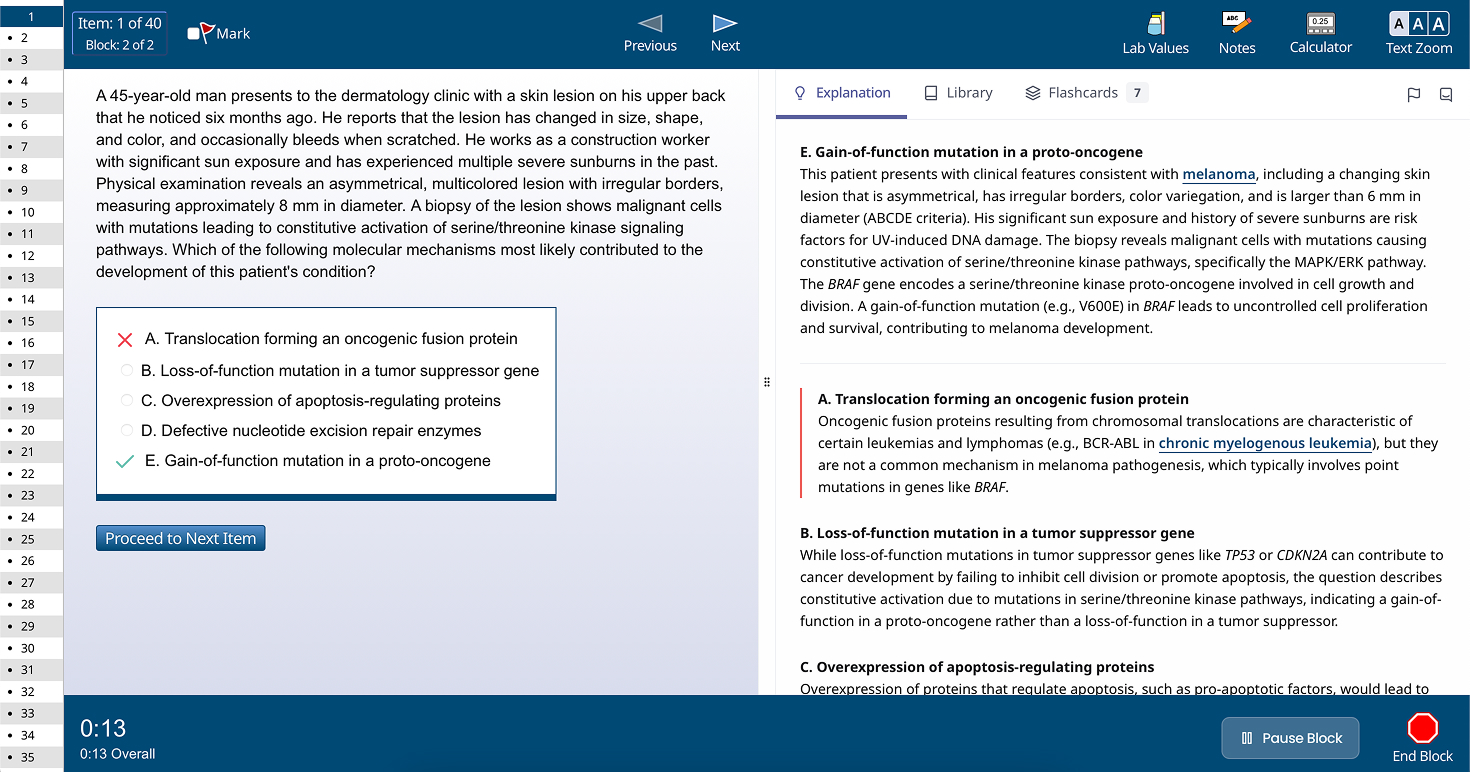
Extracellular deposition of misfolded proteins forming insoluble amyloid fibrils (β-pleated sheets) disrupts organ function. Main types include:
Other types include Aβ2M amyloidosis in long-term dialysis patients and localized amyloidosis (e.g., Alzheimer's disease).
Other features may include macroglossia, hepatomegaly, carpal tunnel syndrome, and easy bruising (e.g., periorbital purpura).
Assessment of organ involvement includes echocardiography (cardiac dysfunction), urinalysis (proteinuria), and nerve conduction studies (neuropathy).
Supportive care for organ dysfunction includes diuretics for heart failure, ACE inhibitors for proteinuria, and medications for neuropathic pain.
Download Ora on iOS or Android and learn wherever you are.

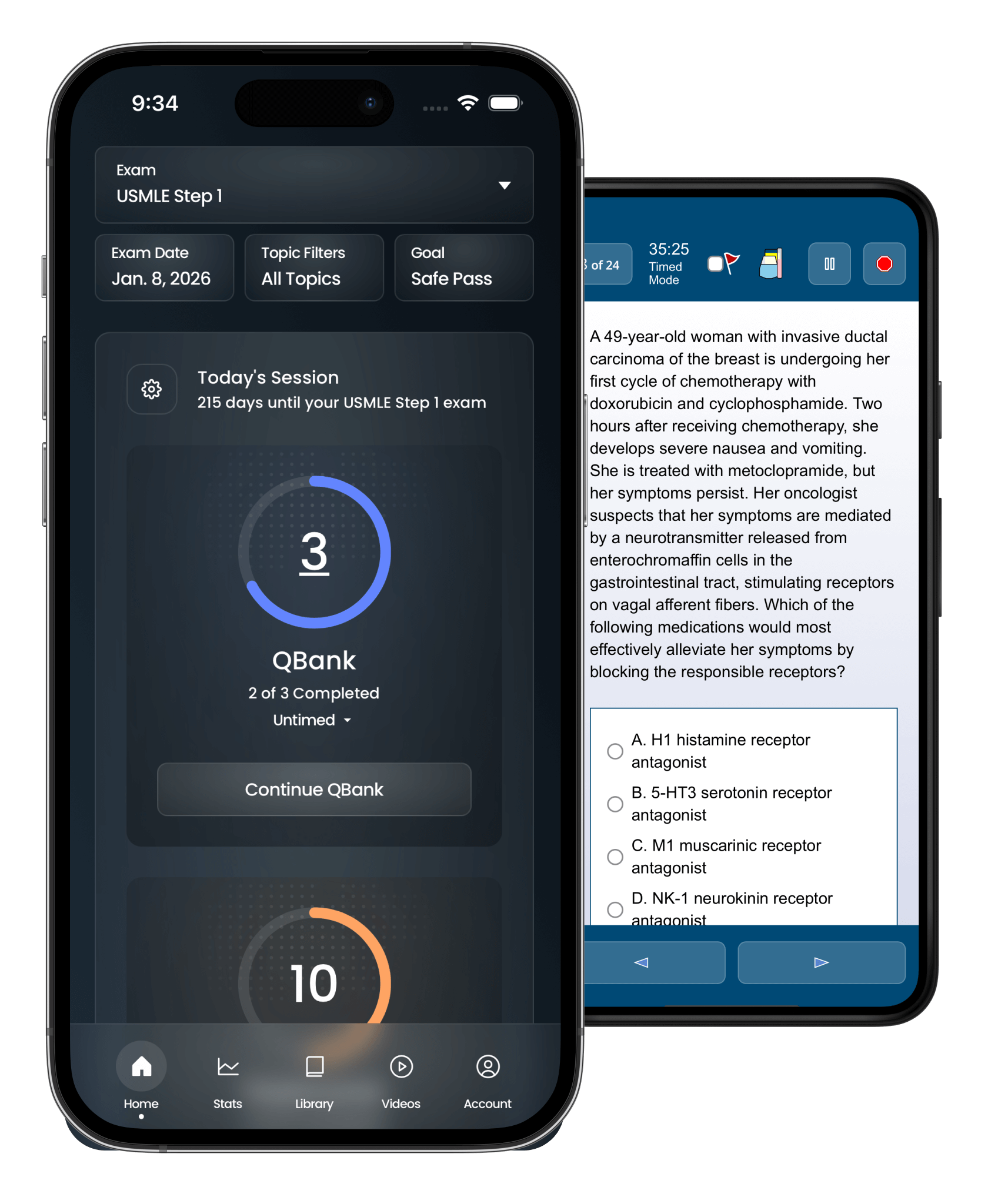


USMLE Step 1 & 2, and all eight NBME shelf exams. We cover all 1,400+ topics on the Official USMLE Content Outline.
Ora also supports studying for school-specific/in-house exams.
COMLEX I & II are currently supported in beta.


In a recent RCT, Ora users improved three times more than UWorld users. Ora is currently working on a paper to publish the results.
- Ian Torchia, M1 at Central Michigan University


The hardest part of step and shelf prep is knowing how and what to study. Ora handles that for you.
Based on your goal, exam date, and topic performance, Ora creates a personalized daily study session to make sure you know every topic by exam day.


We fully respect the copyright and intellectual property of your school and your uploads. Uploaded documents are only used to match and suggest Ora-owned QBank questions, flashcards, and videos relevant to your materials. Here's how we protect your content:


Ora was founded by Ryan Phelps MD during neurosurgery residency at Stanford. In medical school at UCSF, he scored in the 100th percentile on the USMLE, but wanted to build a unified, data-driven platform to make studying less stressful for future med students.
He teamed up with his childhood best friends, Kevin Bastoul (an AI EdTech engineer) and Jacob Caccamo (a HealthTech UX designer) to build Ora.
Since founding, over 100 medical students and doctors have joined the team to help with content validation and product roadmap decisions.