Designed by doctors. Backed by research. Powered by AI.
Welcome to the era of simplified, personalized learning.

Join students from top medical schools on Ora



Focus on your weaknesses—not your strengths.
Over 12,000 QBank questions and 25,000 flashcards. Written by physician-trained AI.
Learn about content on OraDesigned to directly mirror the real test environment
A modern experience for spaced repetition flashcards
Ora learns your knowledge and memory patterns to design an optimal study session each day.
When you finish, you can relax until tomorrow.
Ora schedules related flashcards for review when you answer Qbank questions incorrectly.
Integrated study sessions lead to faster learning and higher retention.
Ora has over 300 videos to help you learn the fundamentals of medicine.
AI chat is integrated right into the QBank and flashcard experience,
making it easier than ever to get your questions answered.
Explore a meticulously curated repository offering an extensive collection of medical education content, designed to support your learning journey.
Explore the Library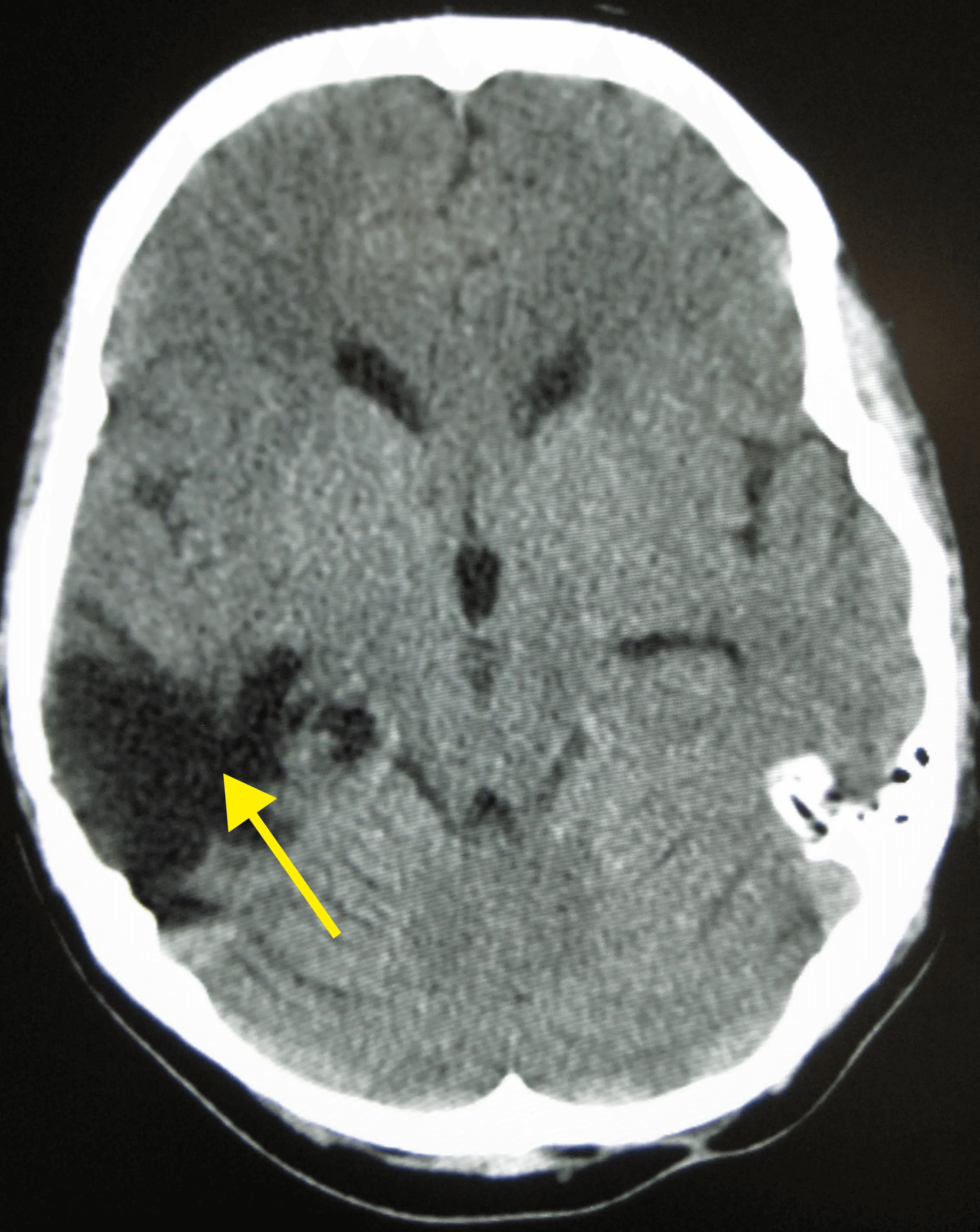
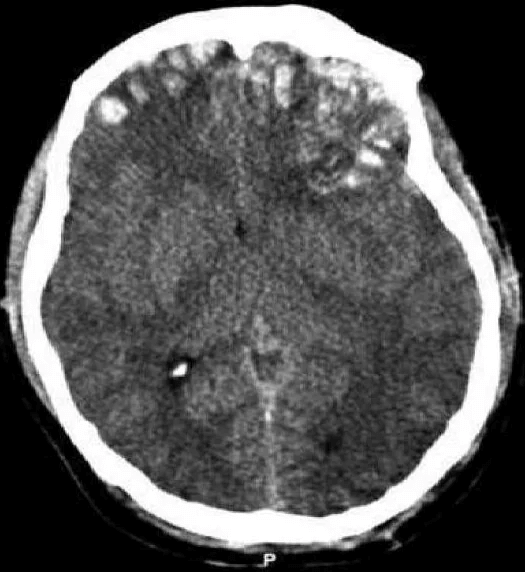
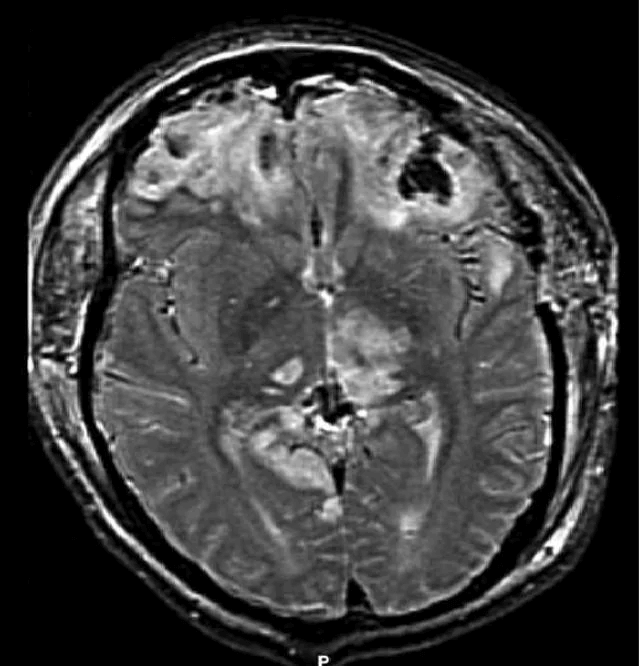
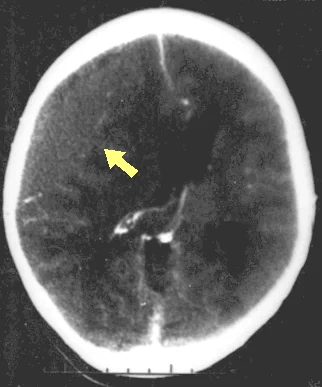
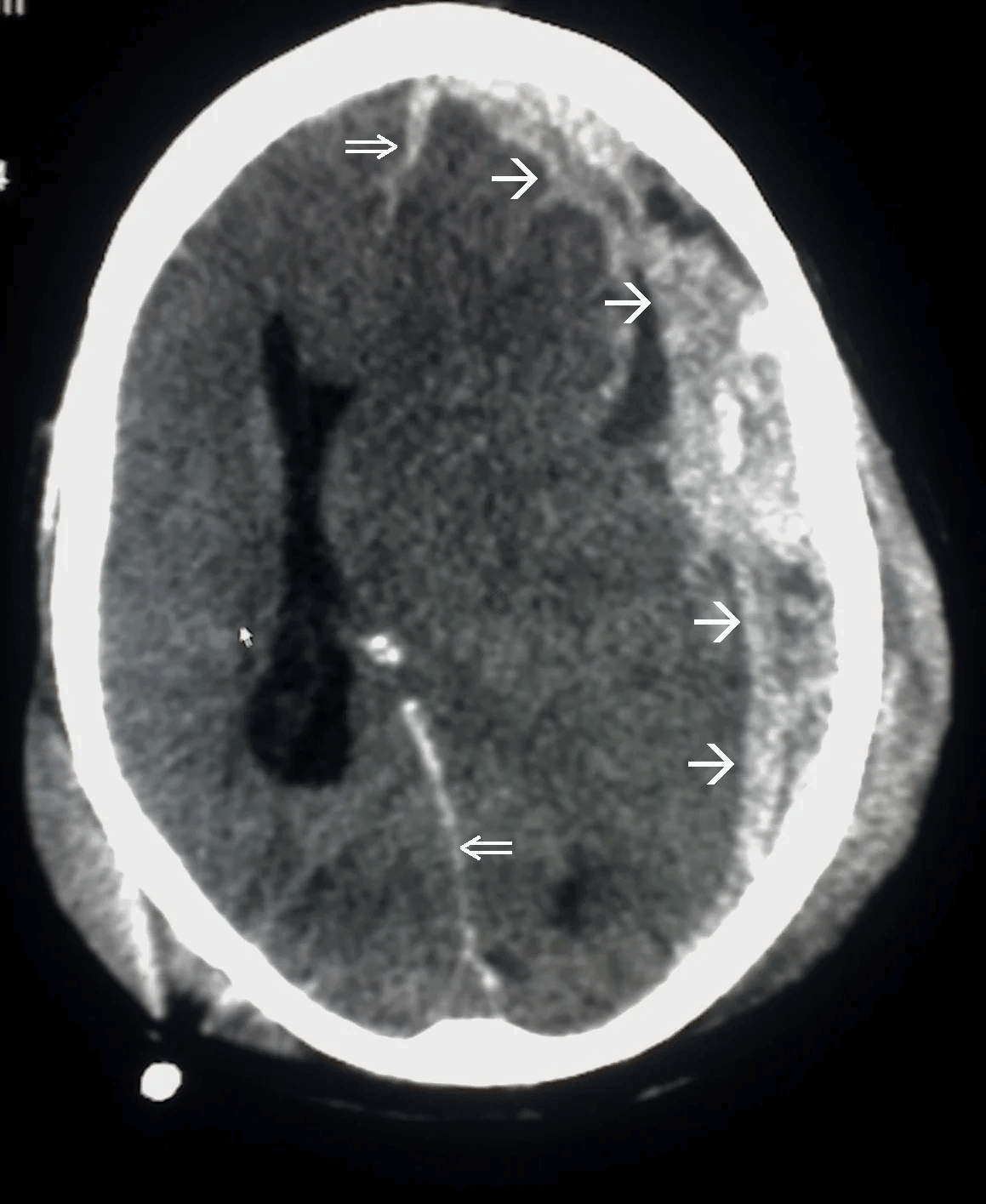
Disruption of brain function due to external mechanical force, involving:
These processes lead to neuronal damage, cerebral swelling, and compromised cerebral perfusion.
Other features may include seizures, vomiting, altered mental status, and signs of skull fractures (e.g., CSF rhinorrhea).
Additional workup may include MRI for diffuse axonal injury, laboratory tests, and intracranial pressure monitoring.
Preventing secondary injury involves maintaining adequate blood pressure, seizure prophylaxis, and temperature management.
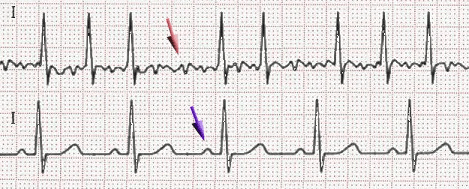
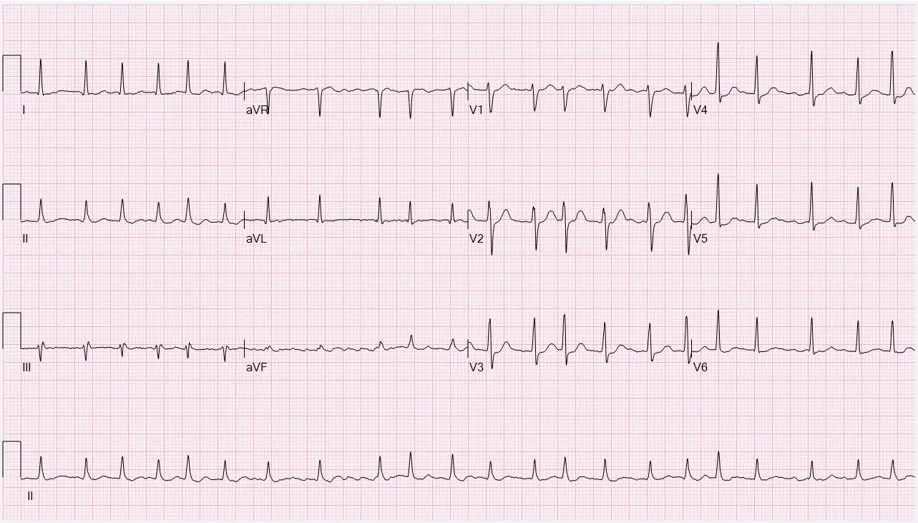
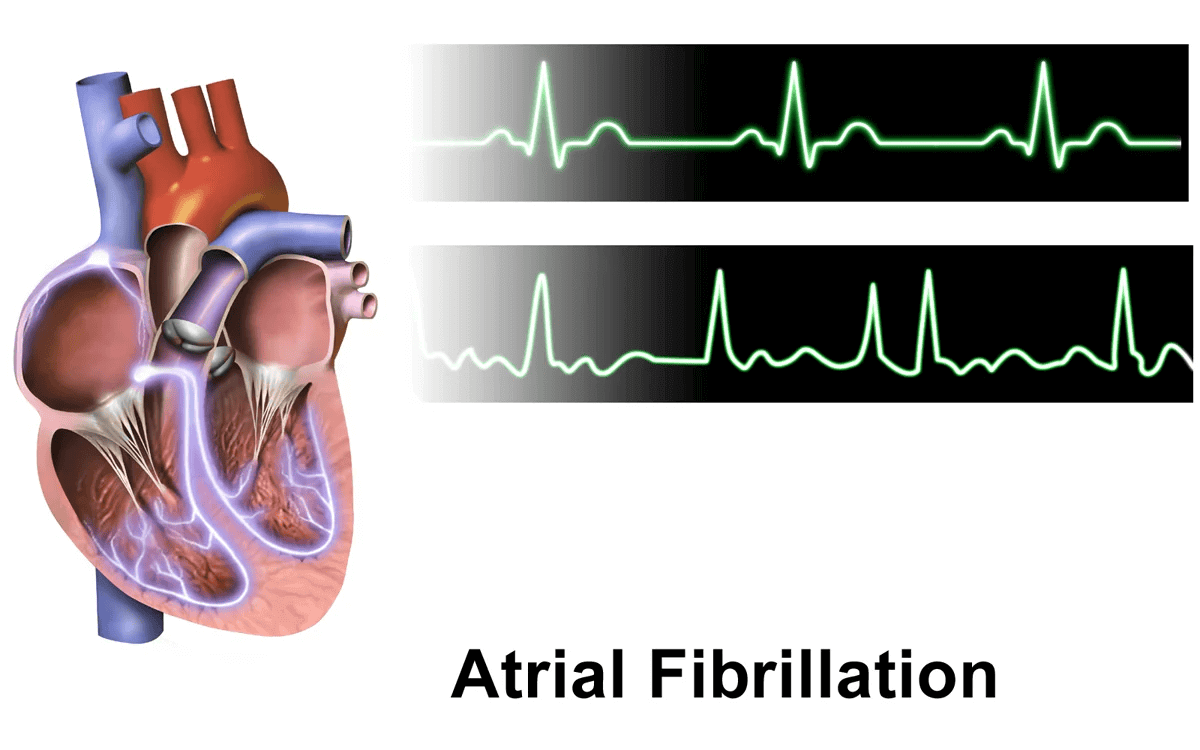
Uncoordinated atrial activation leads to ineffective atrial contraction and an irregularly irregular ventricular response. Key mechanisms include:
Electrical and structural remodeling of the atria promote AF persistence ("AF begets AF").
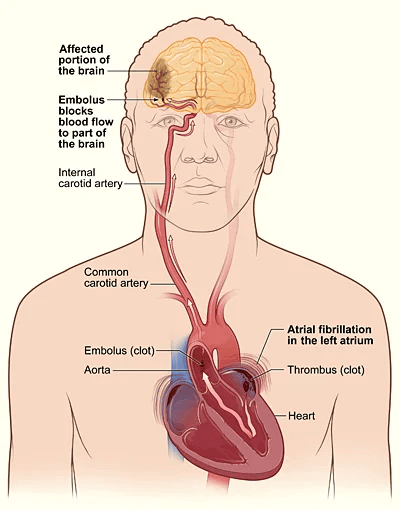
Patients may also experience dizziness, chest discomfort, or be asymptomatic. AF increases the risk of thromboembolic events, such as stroke.
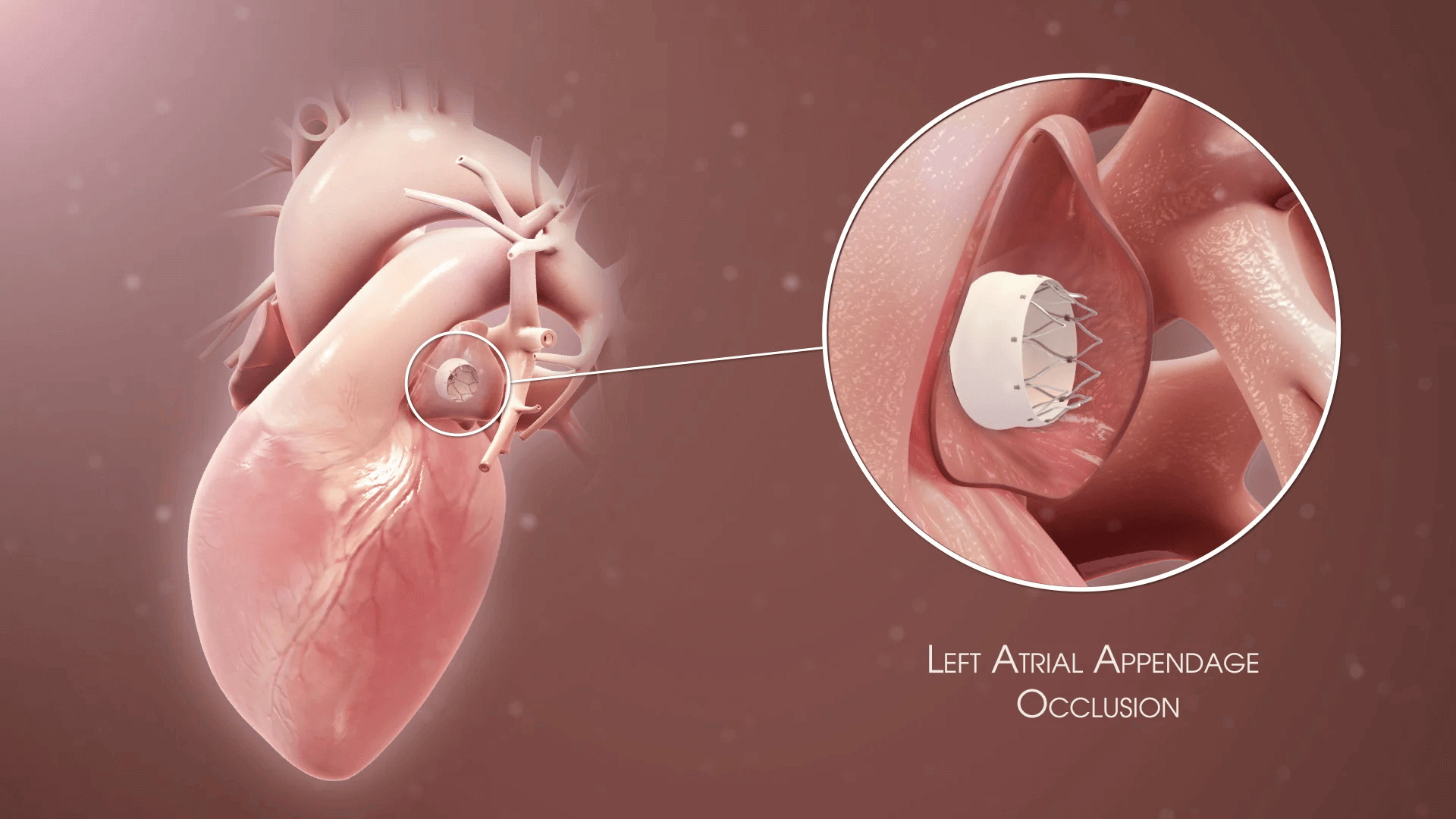
Additional tests include thyroid function tests and evaluation of stroke risk using the CHA2DS2-VASc score.
Rhythm control with antiarrhythmic drugs, electrical cardioversion, or catheter ablation may be considered in symptomatic patients or those with heart failure.
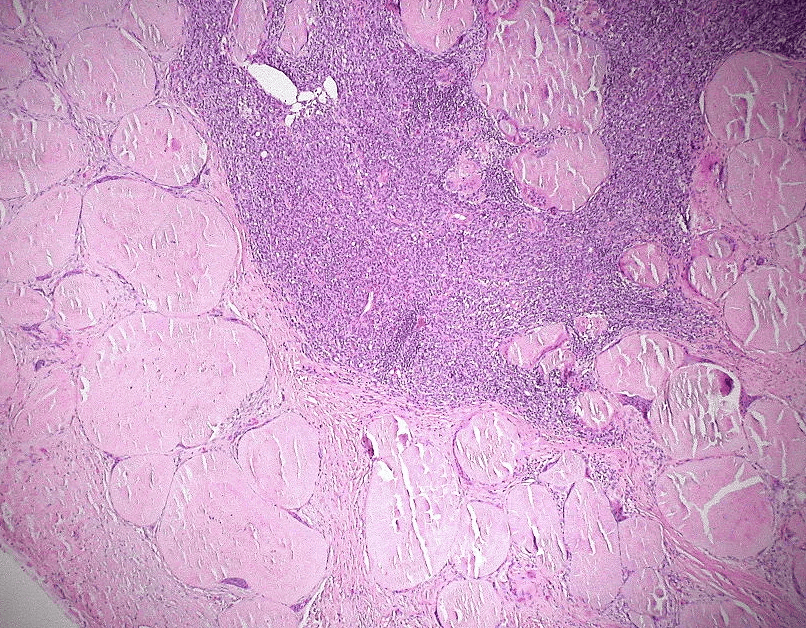
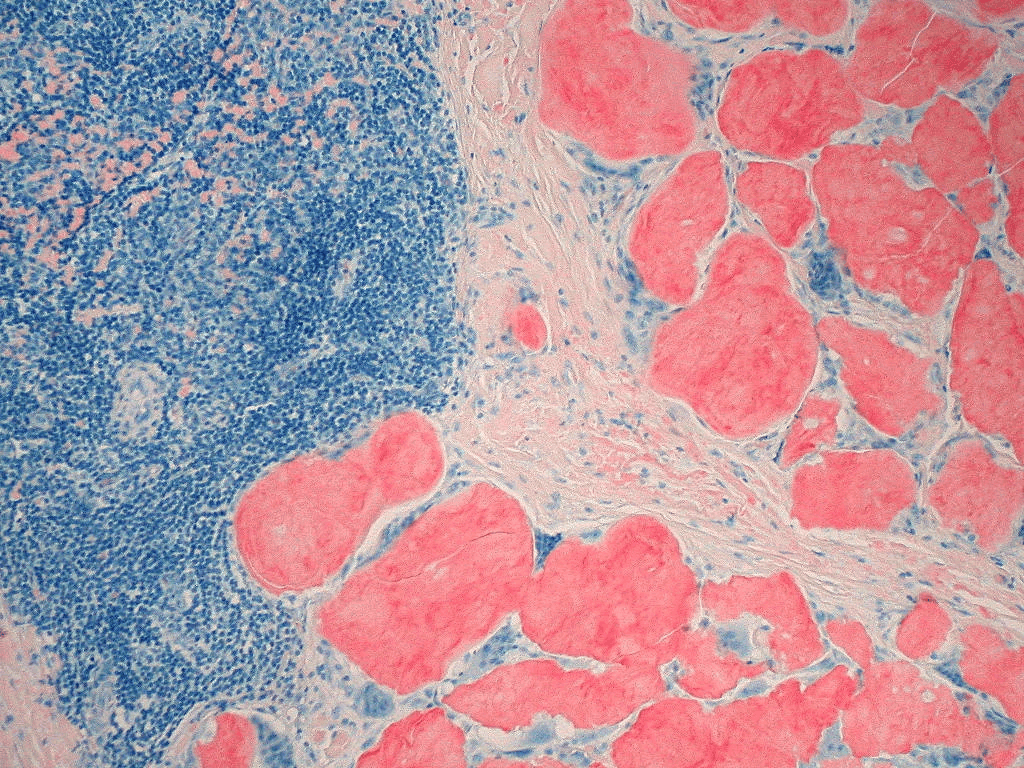
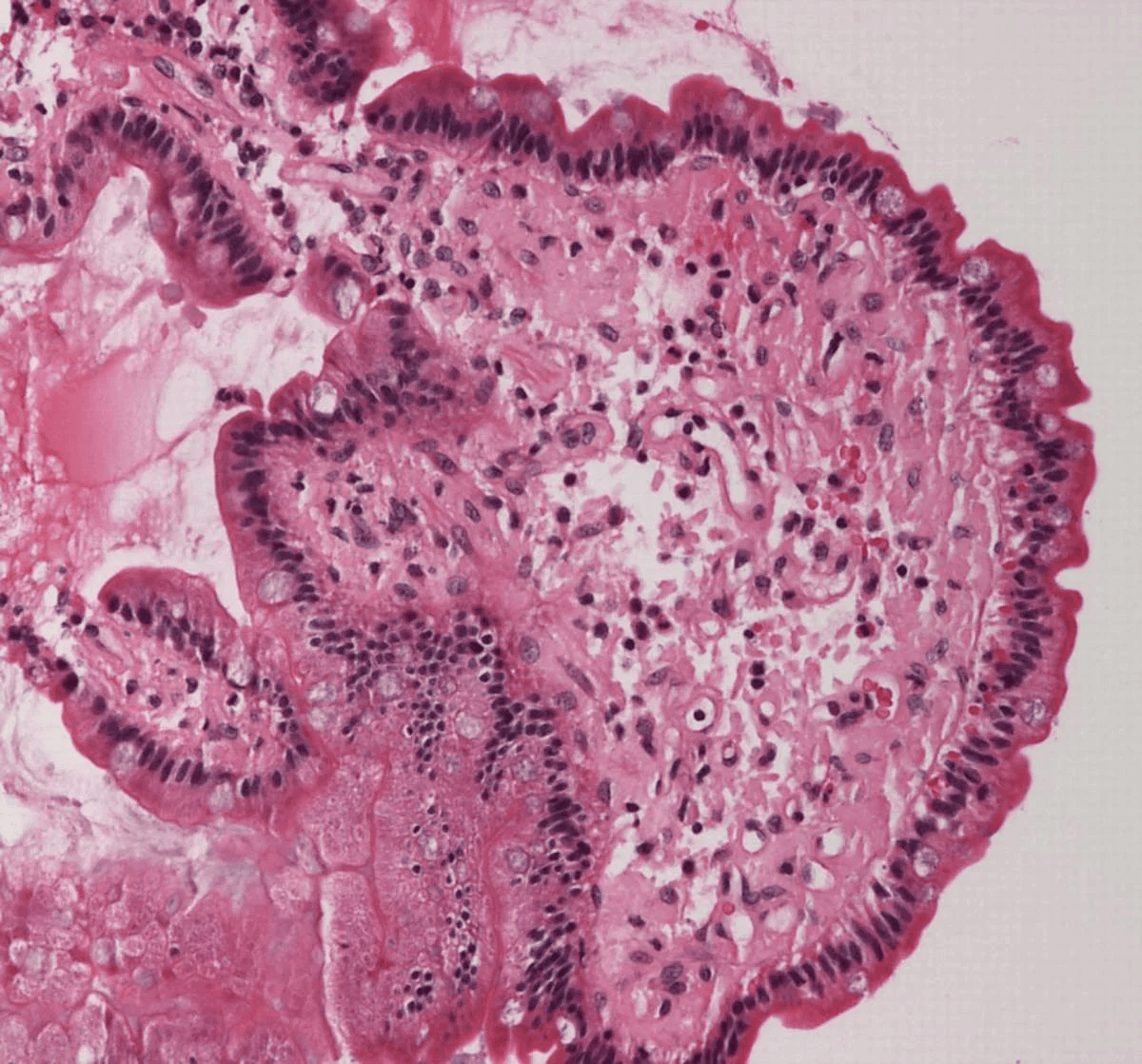
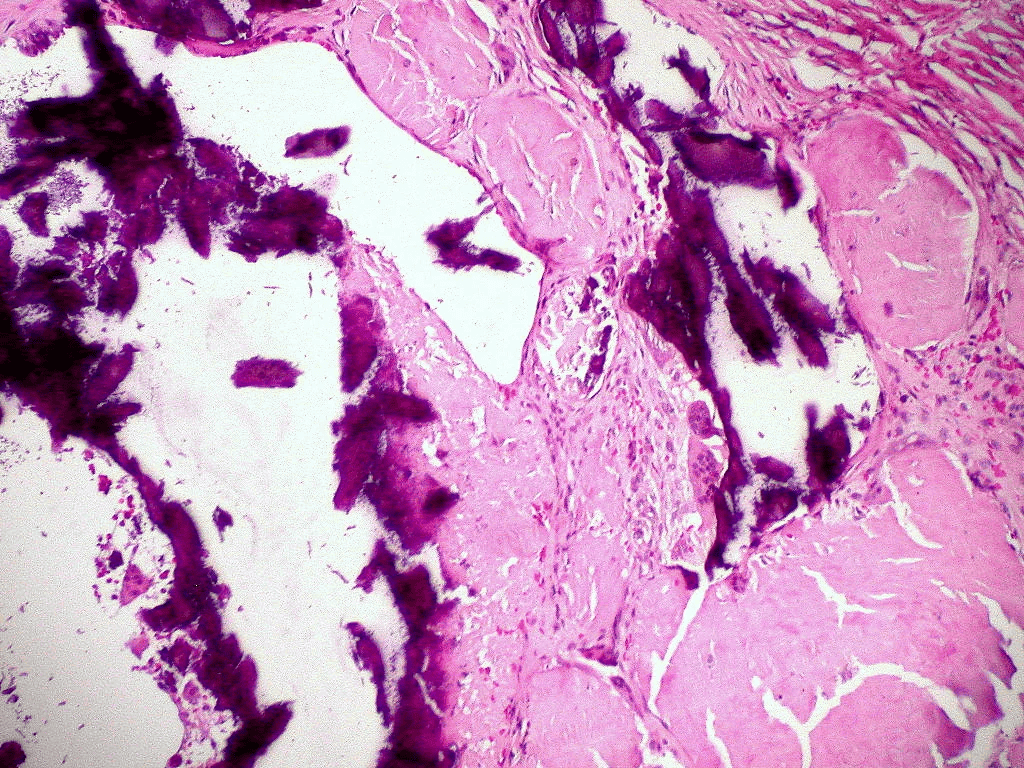
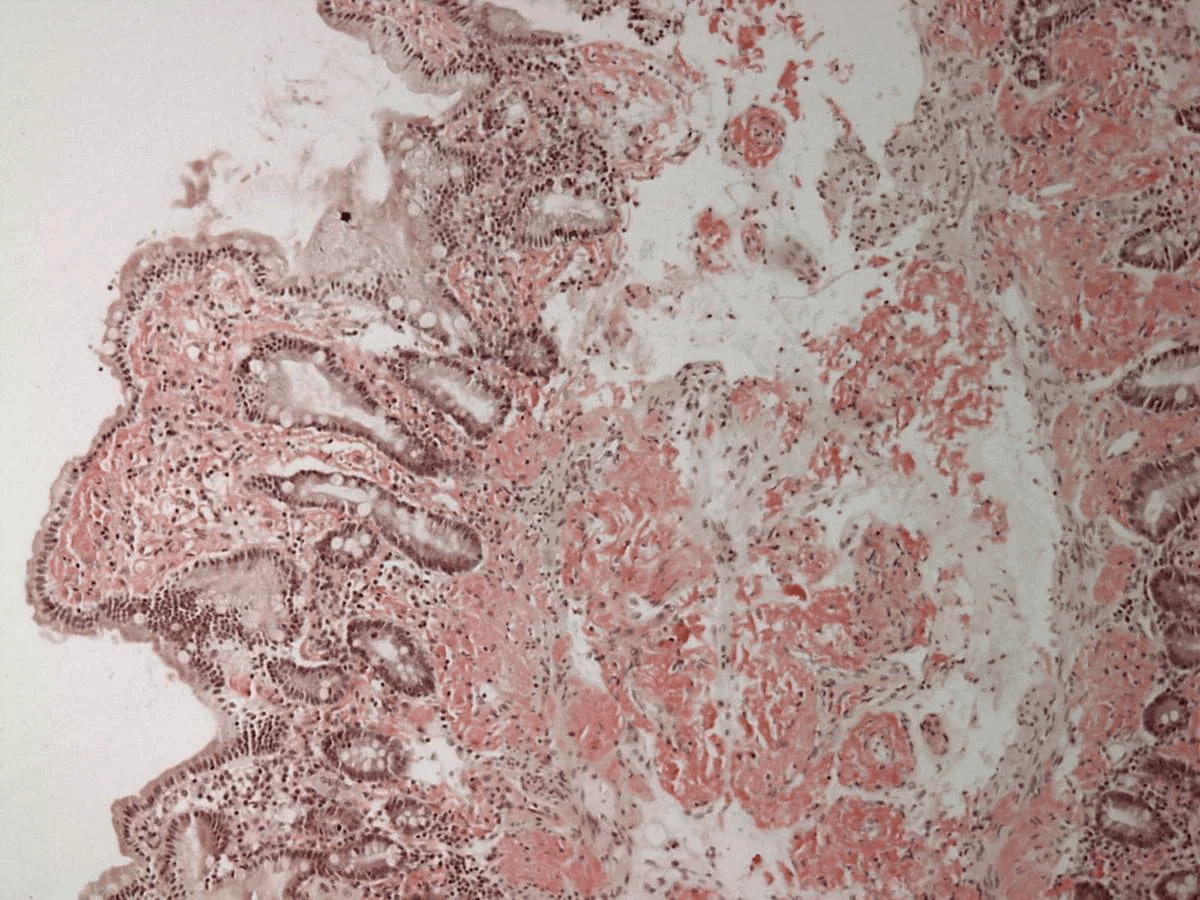
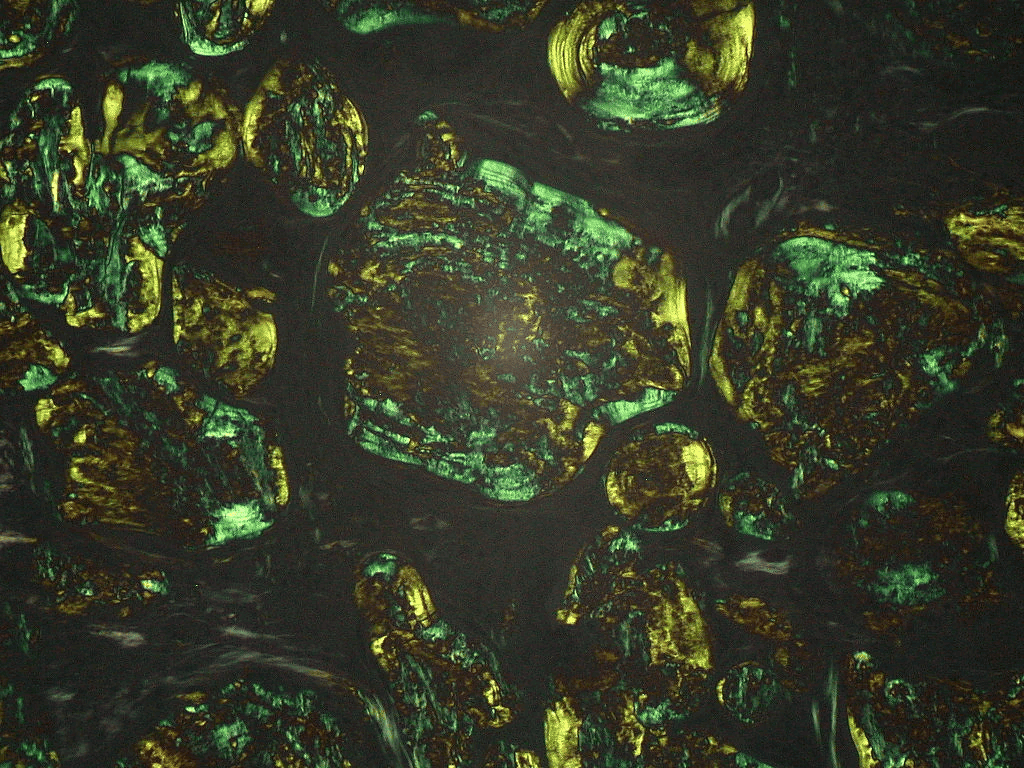
Extracellular deposition of misfolded proteins forming insoluble amyloid fibrils (β-pleated sheets) disrupts organ function. Main types include:
Other types include Aβ2M amyloidosis in long-term dialysis patients and localized amyloidosis (e.g., Alzheimer's disease).
Other features may include macroglossia, hepatomegaly, carpal tunnel syndrome, and easy bruising (e.g., periorbital purpura).
Assessment of organ involvement includes echocardiography (cardiac dysfunction), urinalysis (proteinuria), and nerve conduction studies (neuropathy).
Supportive care for organ dysfunction includes diuretics for heart failure, ACE inhibitors for proteinuria, and medications for neuropathic pain.
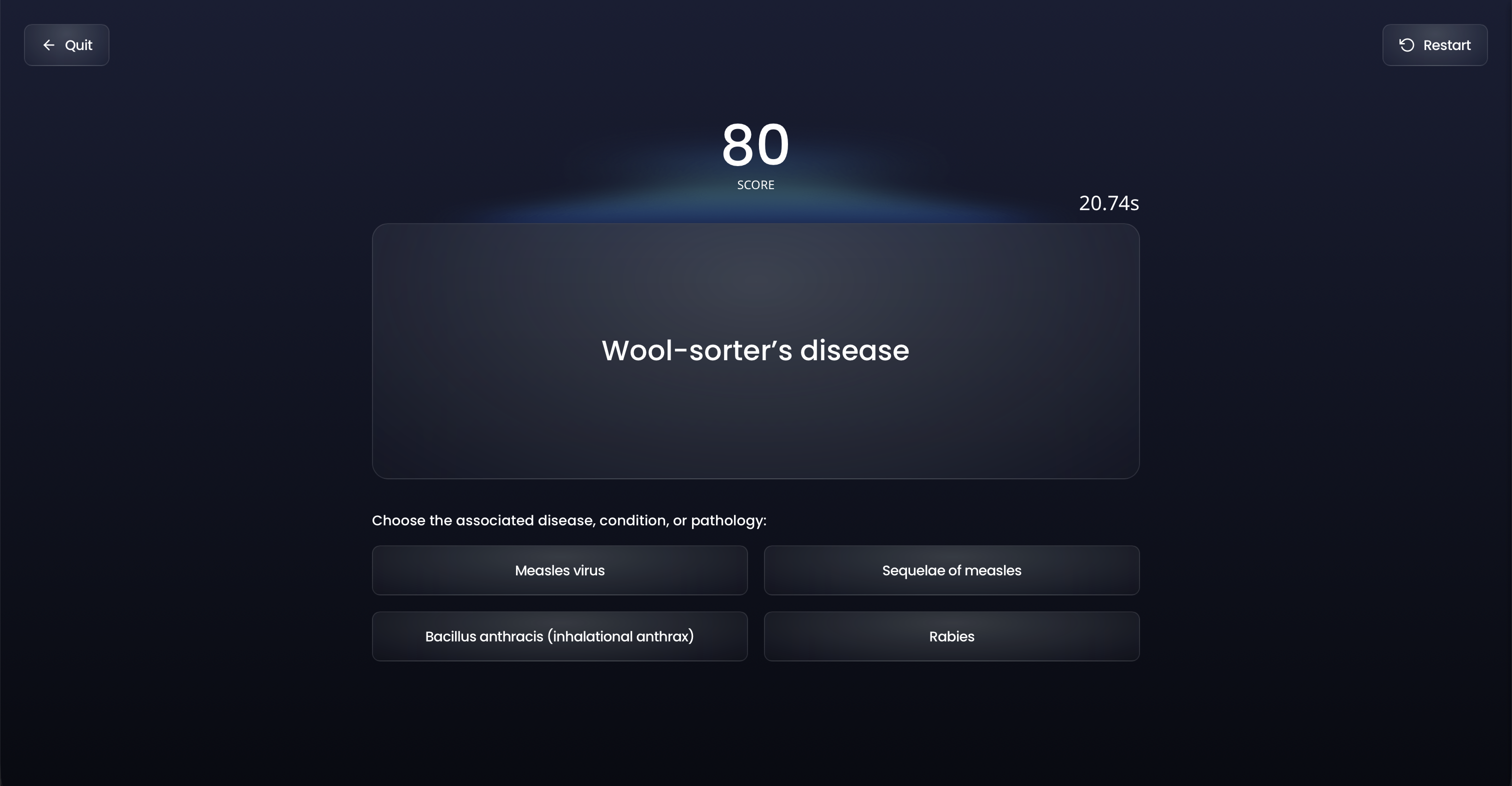
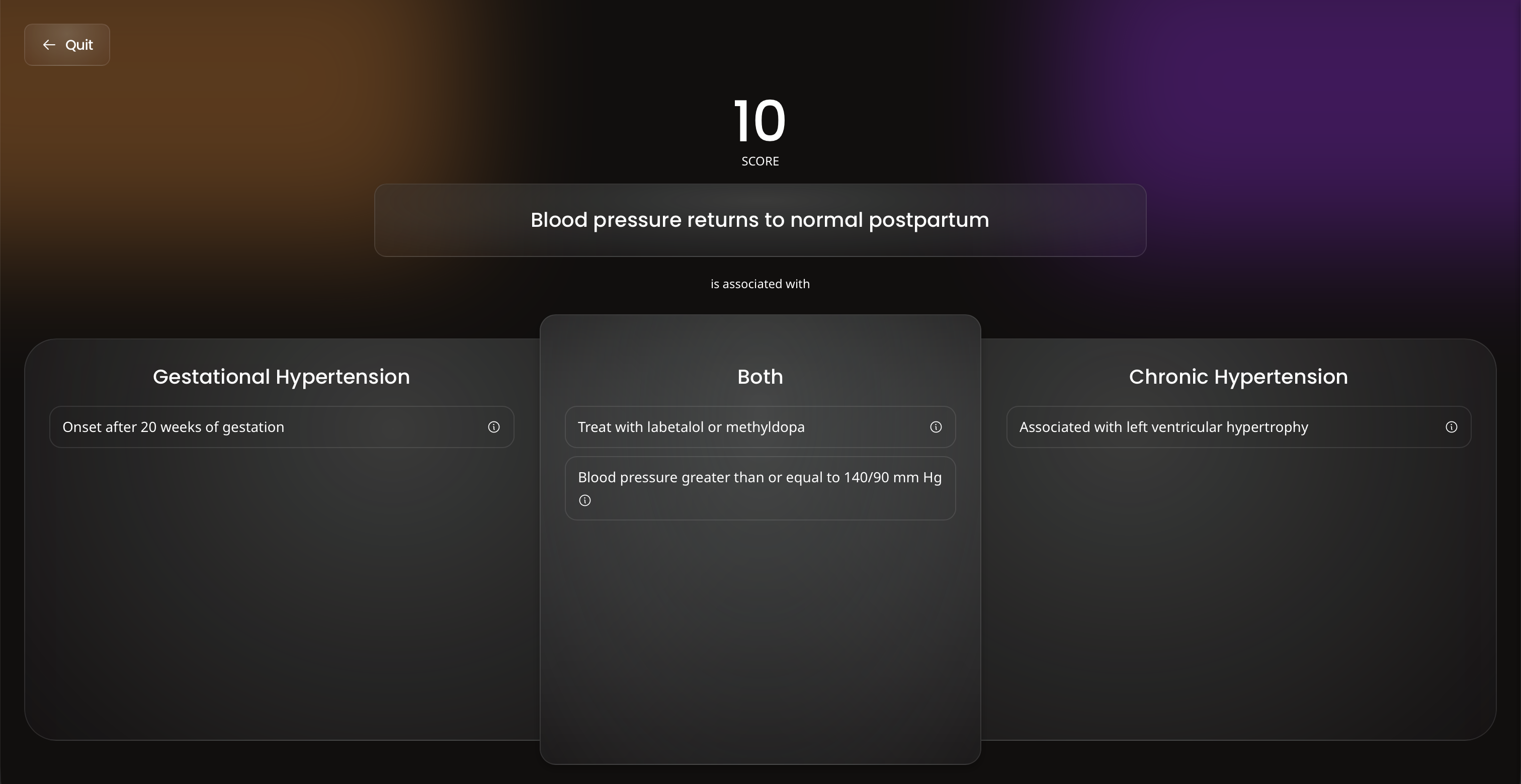
When you need a break from traditional study, flex your competitive side with Ora's games.